Carol Rizzo Hopkins, 81, lived in Four Mile Run until moving to upper Greenfield at age 14. She clearly remembers a network of trails on the hillside. “Everywhere was a path, and we walked everywhere—Schenley Park, Squirrel Hill, Beechwood Boulevard, Magee Swimming Pool. We could be anywhere in two minutes.”
“Growing up in The Run was the best time of my life,” she told me during an in-person interview in December. “It was like a little village for us.”
But the Parkway changed all that. Now, as the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (known as PennDOT) gets started on plans to improve the Parkway East Bridge over Four Mile Run, residents face the prospect of history repeating itself.
On Dec. 1, District 5 City Council member Barb Warwick posted on Facebook that PennDOT is conducting a feasibility study to explore their options for fixing or replacing the six-span bridge.
One option the department is considering involves building a new bridge beside the existing one — similar to their plan for the Commercial Street Bridge on the other side of the Squirrel Hill Tunnels. PennDOT would destroy the existing bridge and move the new bridge in to replace it. Using this method in The Run might shorten closure time on the Parkway East, but it may displace households near the bridge.
Two neighbors, Judy Gula and Ms. Hopkins, witnessed the original construction of the Parkway East bridge from 1949 to 1952.
Life in the Parkway’s shadow
Ms. Gula, 76, has lived in The Run her entire life — just like her father did. In her earliest memories, the Parkway was already under construction.
“We used to roller-skate on the Parkway before it was finished,” she recalled during an interview in December. “Kids rode their bikes and played up there. The construction workers would give us their empty pop bottles and we’d fight over who got them.”
Neighborhood children exchanged those bottles for two cents at Mary Kranyak’s candy store on Saline Street.
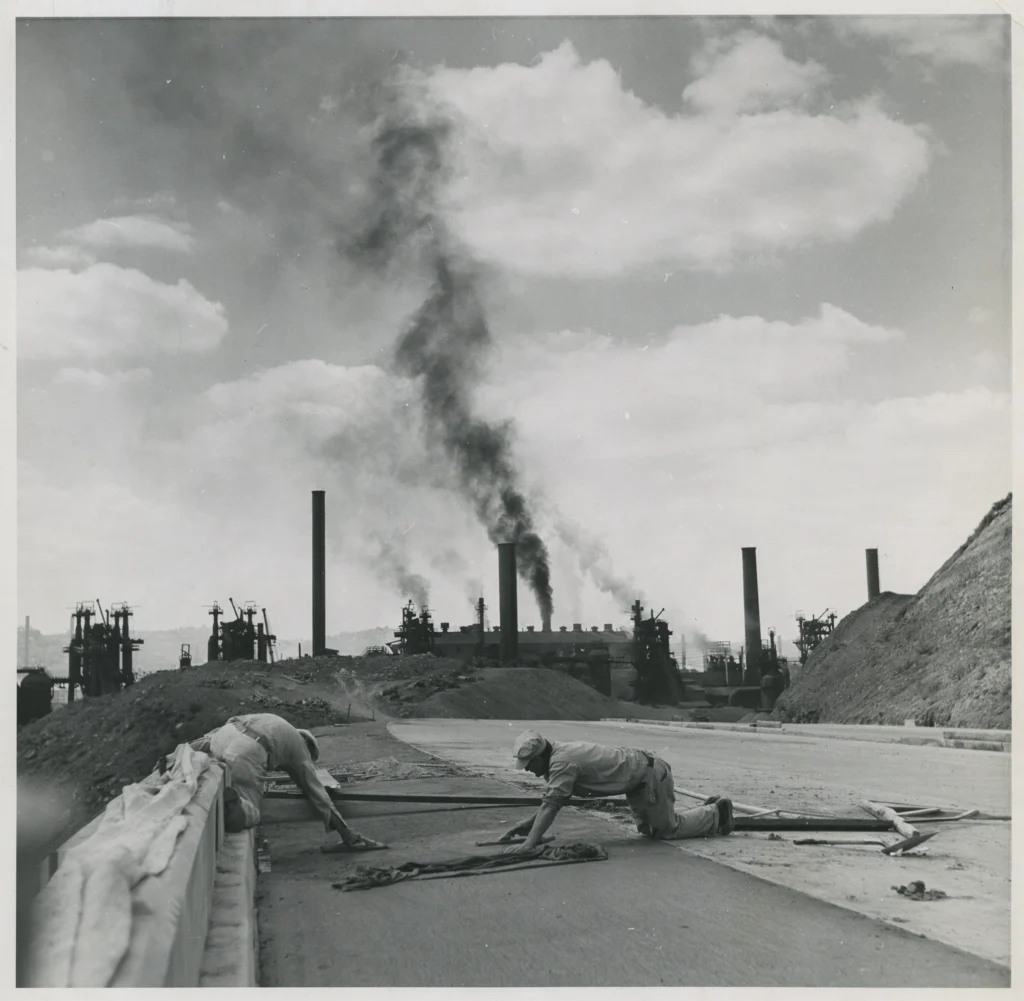

Even after the Parkway opened, non-vehicular traffic continued for a time. Locals used it in ways people might find hard to imagine today.
“My dad and I would walk up to the Parkway to watch cars,” Ms. Gula said. “It was always backed up, even then.” As high school students, she and her friends would “walk the Parkway” to get to Allderdice.
Ms. Gula grew up in the shadow of the Parkway and with shadows of what it replaced. A school behind the apartment building where she lived was torn down, but she isn’t certain whether that was because of construction.
“My mother said there were steps from [The Run] to the Bridle Path [in Schenley Park] that were taken away by the Parkway,” Ms. Gula recalled.
She also remembers older relatives remarking how much quieter the neighborhood had been before the Parkway. Along with the wall of noise produced by speeding cars and trucks, the road brought other problems that continue into the present.
“We used to get all the water from the Parkway down here,” said Ms. Gula, who lives in the eastern part of The Run near the end of Saline Street. “Water used to come up to my [front] gate.”
About five years ago, crews added large rocks to slow water down in the area at the end of the street and behind the building colloquially known as “the pump house.” Ms. Gula says that has helped.
“It just destroyed us”
Ms. Hopkins’ grandmother, who lived on Naylor Street, had a small farm in the field beneath the Greenfield Bridge. The family’s seven children, including Ms. Hopkins’ father, took turns walking their cow to a nearby field to let it graze. By the time Ms. Hopkins came along, her grandmother no longer had the cow, but she still raised chickens.
The field near the pump house where the cow once grazed served as the local playground until Parkway construction began.
“They put all their equipment on our playground,” Ms. Hopkins said. She described large, hollow cylinders that looked like pipes wrapped in metal coils.
“I broke my arm,” she recalled. “I was running at nighttime, and I tripped over a coil lying on the ground. We couldn’t play there anymore.”
Of the displaced families and businesses, Ms. Hopkins remembers three in particular: the Marbella family, a market called Husky’s, and her friend Peggy. Peggy’s family lived in a stylish house with a lot of latticework.
“That’s where a pillar is now,” Ms. Hopkins said.
Ms. Hopkins and her friends and cousins from The Run still talk about the experience of having a highway carved through their idyllic neighborhood. “It affected us kids, and I’m sure the grownups,” she said. “People had cracks in their walls [from the construction] they had to fix.”
Follow this project
Councilmember Warwick encouraged people to sign up for notifications from PennDOT about the bridge project as it moves forward. She said the PennDOT team expects to have the first public meeting on its feasibility study in mid to late summer of 2024. Until then, she promised to include any new developments in the District 5 newsletter and the Facebook page for The Run.
Visit PennDOT’s project page for the feasibility study at http://tinyurl.com/Parkway-East-4-Mile-Run to see more details and instructions for getting project notifications. Visit the District 5 newsletter webpage at https://pittsburghpa.gov/council/d5-newsletters to sign up for monthly emails.

Recent Comments