Cutting the 56 bus would strand some Lincoln Place residents
Editor’s note: This article is the third in a series on how changes proposed in the first draft of the Bus Line Redesign project for Pittsburgh Regional Transit (known as PRT) would affect riders in neighborhoods The Homepage serves.
Most of the Lincoln Place residents interviewed for this article said they no longer ride the bus, either because they work from home or because they found other forms of transportation. But others said they depend on the bus so much, the proposed redesign would change every aspect of their lives for the worse.
A bus line can be a lifeline
Tom Weber, 68, catches the 56 bus on Mifflin Road north of Interboro Avenue.
“Thankfully, the city has a pretty decent bus system that serves 90–95% of my transportation needs,” he said on Dec. 18.
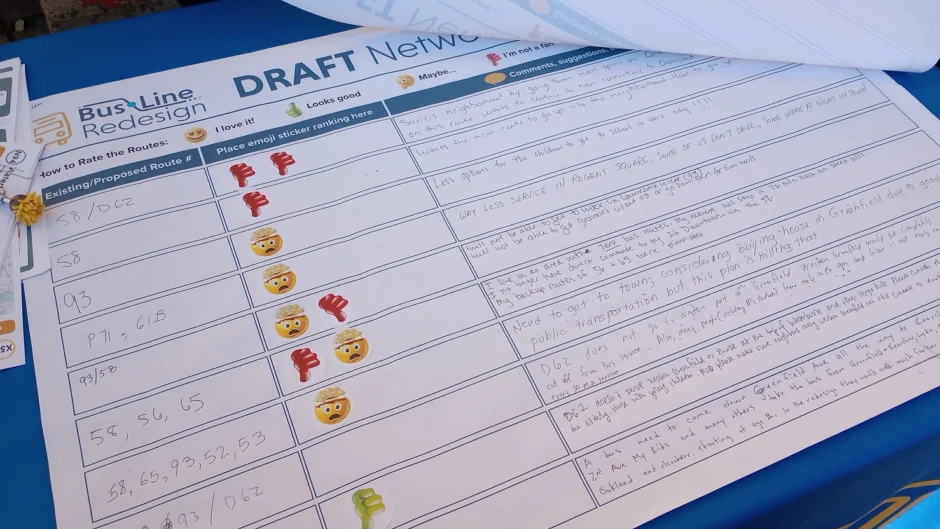
But in the current version of the Pittsburgh Regional Transit redesign plan, the 56 would be eliminated and replacement routes would not serve this part of Lincoln Place. This spring, PRT will publicize a new draft of proposed changes they are calling “draft 2.0.”
Mr. Weber does not own a car and lives on a fixed income. He already walks a steep road to and from the bus stop. The proposed plan would leave him with only one transit option: Walk farther to catch a bus that would not take him to the places he needs to go.
Mr. Weber is always on the move, often riding the bus seven days a week. He volunteers at a church in Homestead. He is deeply involved at the Hazelwood Healthy Active Living Center and spends most weekdays there.
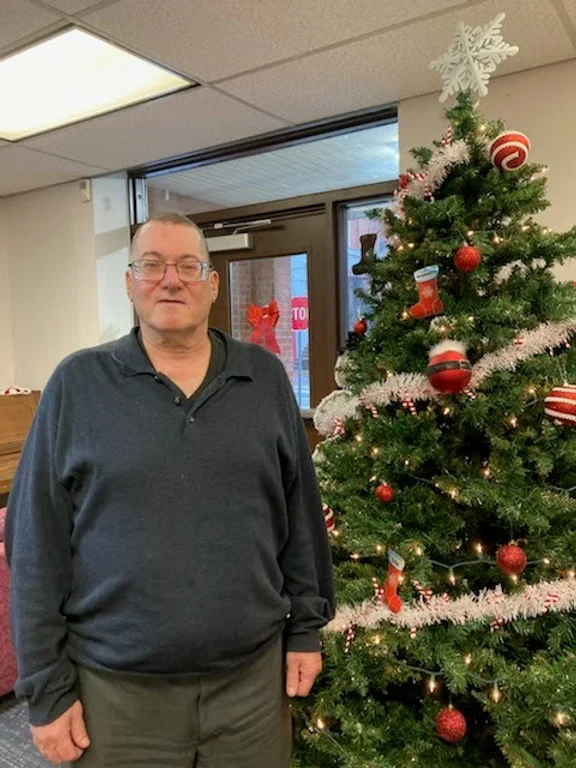

“The only time I don’t come in here [the Hazelwood Healthy Active Living Center] is when I have a doctor’s appointment,” he said. Mr. Weber sees specialists in places as far away as Elizabeth and Jefferson Hills. The 56 allows him to transfer to the routes he needs to get to all his appointments.
“These things are an integral part of my life,” he told me. “Without the 56, I’m at home 24/7.”
Mr. Weber, who said he has a history of depression, credits his busy schedule with keeping him healthy and happy during his retirement. “My involvement here at the center has basically saved my life. I’m able to do so much because my mental health has been so good from being active. It’s a circle.”
The devil is in the data
Laura Wiens, executive director of Pittsburghers for Public Transit, says one reason for the apparent disconnect between PRT’s plan and riders’ needs is the way PRT collected data for its first draft. In a Dec. 16 phone call, Ms. Wiens described the approach as “total amnesia about the system that exists, that people use it — and we have data based on that system.”
Instead of using trips taken on existing bus lines as a starting point for their plan, PRT used cell phone travel data to find the top destinations and origins in Allegheny County. This approach overlooks how people use public transit and cars for different purposes.
“Transit is not a shuttle service,” Ms. Wiens said. “It’s not just drawing a line between places, it’s about connecting people to as many destinations and origins as possible.”
Pittsburghers for Public Transit has been analyzing PRT’s current proposal and has identified changes needed to make a Bus Line Redesign that works for everyone, she said.
First, the changes should increase ridership while recognizing that the people who need public transit most are those who already use it.
“Non-disruption of existing riders needs to be a priority,” Ms. Wiens stressed. That includes avoiding adding transfers to current trips as much as possible. Transfers make trips longer and less reliable, no matter how well-appointed the transit hub is. And for cash users, transfers are more expensive.
In addition, PRT should make the transition simpler for riders by doing less and slowing down.
“It’s impossible for riders to respond [to the plan] because they are doing so much at one time,” Ms. Wiens said. “Since the routes, bus line names, frequencies, and number of transfers are all changing, it’s hard to answer the question, ‘What’s going to happen to my ride?’”
Mr. Weber echoed Ms. Wiens’ comments. “The main reason it’s so confusing is that they’re trying to change everything at once.”
Mr. Weber said he has worked hard to understand the proposed changes, including attending the Hazelwood community meeting.
“This morning I spent an hour and a half tracing routes to find dead spots and consider alternatives. Electric bikes aren’t cheap,” he added.
Similar problems for students
Like others in Greenfield and Hazelwood, Lincoln Place high schoolers use PRT buses to get to school. In Lincoln Place, students have farther to travel to get to schools like Allderdice located across the river. School commutes can go the other way, too.
A school guard who asked not to be named wrote in a Dec. 3 email that the school bus shortage has meant more and more students are riding PRT to school. “I brought this up at a PRT thing in Squirrel Hill and the gentleman said something to the effect of, we can’t plan on or around public school students. [Pittsburgh Public Schools] pays for a lot of those kids to ride the bus, why is their money no good?”
Emily Provonsha, PRT’s manager of service development, said after the Nov. 12 Hazelwood community meeting that PRT had met with school transportation directors from across Allegheny County. PRT asked the schools to share data on where their students travel to and from to reach school so PRT can compare those trips with the transit network.
Help push for a better ‘draft 2.0’
You can review the Bus Line Redesign proposal, get the latest on meetings, and comment to PRT at engage.rideprt.org/buslineredesign/buslineredesign-home. PRT said online comments will remain open until at least Jan. 31.
Pittsburghers for Public Transit is encouraging people to join them in advocating for a Bus Line Redesign that works for all. Visit pittsburghforpublictransit.org/petition-we-deserve-a-prt-bus-line-redesign-that-works-for-us-all/ to read and sign their statement detailing what PRT should do to improve the plan.
“They can get it right in draft 2,” Ms. Wiens said. “But they’ve got to shift some fundamental assumptions.”
This article originally appeared in The Homepage.



Recent Comments